 |
1.
掌握下列词与词组
1. airport

2. separate

3. hotel

4. weekend

5. guide

6. bank

7. villager

8. sharp

9. crop

10. bone

11. soil

12. price

13. mile

14. destroy

15. but prep.

16. future

17. sight

18. be about to

19. take a taxi

20. see…off

21. have a good trip

22. every two years

2. 学习表示“问候、祝愿和应答”的句子
1) Give my regards to sb..
2) Say “Hi / Hello” to sb. from me.
3) Have a nice / good time.
4) Good luck. Have a good trip.
5) The same to you.
6) How about you?
3.
了解现在进行时表示将来时的用法 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
1. Words
And Phrases About Travel

a.
(1) travel:
(2) journey:
(3) trip:

(4) tour:

(5) voyage:
(6) hike:
b.
tourism

tour agency /service

touring party

tourist / traveler

tour guide

travel companion

traveling expenses

route

schedule

2. How can we
travel?
(1) by road / land by bike,
bus, car, taxi, train, on foot, etc.
(2) by sea / water by ship,
boat, etc.
(3) by air by
plane
3. Things
taken while traveling

traveling bag

sleeping bag

tent

sneaker

raincoat

map

flashlight

compass

sun glasses

soap, toothpaste, tooth-brush, towel,
etc.

medicine

food

5. Amazon

(1) Map of Amazon:
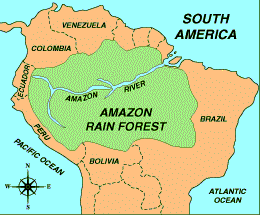
(2) Brief introduction:
Amazon is the longest river in South
America. It is rich in aquatic products. A kind
of
dangerous fish named “piranha”(食人鱼)
live in the river, which often attack people
falling into the river in shoals.
6. words about
rivers

river bank

riverbed

river mouth

river course

river valley

waterways

the bend of a river

riverhead

river transport

river system

branch

7. Types of Forests

tropical forests

rain forests

monsoon forests

coniferous forests

pine forests

broad-leaved trees

windbreak forests

sand-breaks

evergreen trees

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 Amazon
River Amazon
River
The Amazon, about 6,450 km (4,000 mi) in length,
is, after the Nile, the second longest river in
the world. Flowing eastward across Brazil in the
broad equatorial part of South America, it has
the world's largest drainage basin, more than 7
million sq km (2.7 million sq mi) or nearly 5%
of the world's total land area. It carries
nearly 20% of the Earth's total water discharge
to the ocean--more than the six next-largest
rivers combined. The flow is so powerful that it
noticeably dilutes the ocean water of the
Atlantic 160 km (100 mi) beyond the coastline.
The Amazon's headstreams form in the
Peruvian Andes little more than 160 km (100 mi)
from the Pacific Ocean. In 1541 the Spanish
explorer Francisco de ORELLANA began European
exploration here, descending the river to the
Atlantic. In any event, he gave the river its
name, which refers to the AMAZONS of Greek
mythology. Most of the river's drainage basin
lies east of the Andes. It is composed of low
plains less than 150 m (500 ft) above sea level,
strips of floodplain alongside the channels, and
broken higher ground in the upper reaches of its
many tributaries, to both the north and the
south
 Rain
Forest Rain
Forest
Rain Forest, tropical woodland,
characterized by lush (green and growing
strongly) vegetation and great biological
diversity. There are more species of plants and
animals in tropical rain forests than in all the
rest of the world. About 70 percent of all plant
species in these forests are trees.
Most of the world's tropical rain forests
are within 10° of the equator. The largest
tropical rain forests are located in the Amazon
Basin in South America; in southern Asia,
including the large archipelagoes; and in the
Congo Basin in Africa. Tropical rain forests
contain most of the planet's bio-diversity, and
there are probably still millions of insect
species, as well as many plant species, that
have not been described scientifically.
IMPORTANCE It is now generally accepted
by scientists that rain forests are of more
potential value on a long-term sustainable basis
when left more or less intact than when
converted to pastures or other simplified
habitats. Rain forests have built up the largest
standing biomass of any plant community on
earth, and they have done this almost
independent of soil conditions by recycling
nutrients. Managed rain forests can thus provide
huge amounts of valuable timber, retain the
naturally thin topsoil layers, regulate runoff,
and stabilize local climate.
Because rain forests contain the earth's
greatest diversity of plants and animals, they
also represent giant gene banks that can provide
new drugs, foods, and other products.
 HUMAN
IMPACT HUMAN
IMPACT
There are a large number of natural phenomena
and human activities that have had an impact on
rain forests. Cyclones, lightning fires,
disease, landslides, and other natural forces
are now of rather minimal influence compared to
human activities such as logging, road building,
mining, and large-scale clearing for cattle
pasture and other agricultural crops.
Traditional societies practiced slash-and-burn
cultivation in which only relatively small areas
were cleared. After two or three years, when the
nutrients in the soils had been used up, the
land was abandoned and another cleared. In
modern practice, however, the large-scale
clearing that takes place in nearly all rain
forest areas is so extensive that hundreds of
years would probably be needed for anything
resembling the original vegetation to return.
 Since
the 1970s the rate of tropical deforestation has
accelerated greatly. The eastern region, in
places such as Australia, Sumatra, Malaysia, and
Melanesia, began to suffer huge losses due to
timber and agricultural operations. Amazonia,
which became a focus of world attention, was
being cleared mostly for large cattle ranches
and ambitious government programs, such as the
Trans-Amazon Highway. Since
the 1970s the rate of tropical deforestation has
accelerated greatly. The eastern region, in
places such as Australia, Sumatra, Malaysia, and
Melanesia, began to suffer huge losses due to
timber and agricultural operations. Amazonia,
which became a focus of world attention, was
being cleared mostly for large cattle ranches
and ambitious government programs, such as the
Trans-Amazon Highway.
There is growing concern about the loss of
bio-diversity and global warming (due to
increased levels of carbon dioxide) that may
result from rain forest destruction (see
Greenhouse Effect). It now seems clear, however,
that the loss of species is by far the more
important concern. So little is yet known about
rain forest diversity and ecology that
large-scale extinctions could take place as a
result of human activities before anything can
be done to understand the consequences of such
extinctions and prevent them from happening.
 The
Amazon Rain Forest The
Amazon Rain Forest
The Amazon rain forest, with an area of about 6
million sq km (about 2.3 million sq mi), covers
much of equatorial South America and contains
more species of flora and fauna than any other
ecosystem in the world. Trees constitute about
70 percent of the plant species found in rain
forests. Currently, the Amazon rain forest is
being cleared at an alarming rate for timber and
agricultural purposes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
[基础知识]
1. 词法
(1) separate
[说明] separate作形容词时表示“个别的,单独的,分离的,分开的”。
例如:The word has two separate
meanings.
这个词有两种不同的意思。
The children sleep in separate beds.
孩子们睡在各自的床上。
separate还可以作动词用,表示“使分离,分开,隔开”。常用搭配有“separate…from…”
,
作“使……和……分隔”解。
例如:You'd better separate the
good apples from the bad ones.
你最好把好苹果和坏的分开。
North Korea is separated from China
by the Yalu River.
朝鲜和中国由鸭绿江相隔。
(2) by land
[说明] by land表示“走陆地”。介词by可表示“用……”;“借助于……”。
后面可跟表示交通工具的名词,名词前不能加冠词。
例如:I go to school by bike or
by bus, but my father goes to work by car.
我骑车或乘公共汽车上学,但我爸爸开车上班。
注意:当指特定的车辆时要加冠词。
例如:He left by the 10:00
train this morning.
他今天上午乘10:00的火车走的。
(3) see…off
[说明]see…off 表示“为某人送行”。
例如:Thousands of people were at
the airport to see them off.
数以千计的人在飞机场给他们送行。
(4) every
[说明]every可作“每隔”,“每……”解。常用在“every+基数词+复数名词”的结构中。
如果“every+基数词+时间名词”,我们可译作“每……”或“每隔……”。但注意
英汉互译在数字上可能不一致。
例如:The doctor told him to take
the medicine every four hours.
医生让他每四个小时(每隔三小时)吃一次药。
He usually comes home every two
weeks.
他通常每两周(每隔一周)回家一次。
如果“every + 基数词+表示距离的复数名词”,可译作“每……”或“每隔……”,英汉互译在数字上则
是一致的。
例如:We were asked to plant a
tree every twenty meters on both sides of the
road.
要求我们每隔(每)20米在马路两旁栽一棵树。
Change the oil in the car every
5,000 miles.
每跑5,000英里就要换一换汽车里的润滑油。
(5) be about to (do sth.)
[说明] be about to (do sth.)
表示“马上就要(做某事)”或“正要(做某事)”。
例如: The sun is about to sink in
the west.
太阳正要西下。
I was about to go to bed when the
telephone rang.
我正要睡觉,这时候忽然电话铃响了。
(6) but
[说明]but作介词表示“除了……”;
“除……之外”。常和nobody; nothing等连用。
nobody but (= nobody except) 表示“仅”,“除……之外没有其他人”。
nothing but (=nothing except) 表示“仅”,“除……之外没有其它东西”。
例如:Nobody but me knew her
name.
除我之外,没有人知道她的名字。
Nobody else but Peter could ever say
such a thing.
只有彼得才能说出这种话来。
There is nothing in the box but a
piece of paper.
盒子里除了一张纸什么都没有。
[练习题]
1. I was about to leave the
classroom _____ it began to rain.
A. as B. when C.
while D. before
2. ---How are you getting to the
airport?
---We are going to _____ a
taxi.
---Oh, I see. You are getting
there _____ taxi.
A. by, by B. take, take
C. take, by D. by, take
3. ---Why are you going to the
airport with your parents?
---I'm going there to ______.
A. see off them B. see
them off C. meet them D. see them
left
4. He said _____ goodbye when he
left.
A. not anything B.
anything else C. nothing but D.
anything except
5. ---How often do you have your
hair cut?
---______.
A. In a month B. For
three weeks C. Every day D. Every
three weeks
2. 语法句法
(1)
现在进行时可用来表示将来时
[说明]
现在进行时表示将来时,即表示按计划或安排在最近将要进行的动作。
特别是一些表示“移动性”的动词,如:go,
come, arrive, leave, start, fly, get
等,常用进行时表示将来时。
例如:We are staying in Shanghai
for a week.
我们计划在上海呆一个星期。
My father is leaving for Japan next
week.
我父亲将于下周动身去日本。
He is coming back this Sunday.
这个星期日他就回来了。
How are you getting there?
你将怎么到那儿去?
(2) It is (not) + adj. + (for sb. )+ to do
sth.
[说明] 在It is + adj. + (for sb.
)+ to do sth.这个句型中,it
是形式主语,句末的不定式
to do sth.是真正的主语。
例如:It is easy to work out the
problem in this way.
用这种方法解这道题非常容易。
It is impossible for us to finish
the work in three days.
对我们来说三天内完成这项工作是不可能的。
It is not necessary for you to
introduce your friend Cook.
你没有必要介绍你的朋友库克。
(3) …see + 宾语+ doing sth. / do sth.
[说明] 在…see + 宾语+ doing
sth. / do sth.这一结构中,-ing形式和不带
to的不定式都是动词see的复合宾语。但see
+ 宾语+ doing sth.和see + 宾语+ do
sth.在意义上不同。
例如:I see him cleaning the
blackboard.
我看见他在擦黑板。(他正在擦)
I see him clean the blackboard.
我看见他擦了黑板。(从始至终)
从而我们可以看出,see sb.
doing sth. 可以表示“看到某人正在做某事”;而see
sb. do sth.
表示“看见某人做完某事”。
能够用这种结构的还有:hear,
notice, watch 等词。
例如:I heard him singing an
English song.
我听见他在唱一首英文歌。
I heard him sing the English song.
我听见他唱过那首英文歌曲。
(4) It takes + sb. + some time + to do
sth.
[说明] It takes + sb. + some time
+ to do sth.这个句型中的take表示“花费”、“需要”。
全句的含意是“花费某人一些时间做某事”。
例如:It took me two hours to
finish my homework.
我花了两个小时写完了作业。
It usually takes me ten minutes to
get to school.
我一般用10分钟就到学校了。
It will take them more than a year
to complete the building.
盖完这座楼房他们得花一年多的时间。
(5) What +a/an + 名词+主语+谓语!/
How +形容词/ 副词+主语+谓语!
[说明]上述两个句型都是感叹句的句型。当What
+a/an + 名词+主语+谓语!
这个句型中的名词是复数
或不可数时,我们则去掉不定冠词a
或 an。
例如:What a beautiful flower it
is!
这花儿多么漂亮啊!
What beautiful flowers they are!
这些花儿多漂亮啊!
What important news(it is)!
多么重要的新闻啊!
How tall he is!
他真高!
How hard they are working!
他们干得真起劲!
[练习题]
1. I often hear her _____. Listen ,
can you hear her _____in the next room?
A. sing, to sing B.
singing, sing C. to sing, sing D.
sing, singing
2. ______ fine weather it is! Let's
go out to play basketball, ______?
A. What, shall we B. What
a, will you C. How a , will you D. How,
shall we
3. ----How long _____ the journey
take you?
----It took me two days _____
there.
A. does, to get B. does,
getting C. did, to get D. did,
getting
4. Is _____ possible to fly to the
moon in a spaceship?
A. it B. this C.
that D. what
5. My uncle _____ to see me. He will
be here in a minute.
A. comes B. has come
C. came D. is coming |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
[拓展知识]
1. 词法
(1) guide
[说明] guide作名词作“向导”,“导游”,“指南”解。
例如:We need a guide to show us
around the city.
我们需要一个导游带我们参观这个城市。
I think this guide is helpful to
you.
我认为这本指南手册对你有帮助。
除此guide还可作动词用,作“向导”,“指导”,“引导”解。
例如:He guided the tourist party
through the park.
他带领旅游团到公园参观。
Mr. Brown often guides his students
in their studies.
布朗先生经常指导他的学生作研究。
(2) do
[说明]do
作助动词时,不仅可帮助构成一般现在时和一般过去时的疑问句及否定句,
还可用在肯定句和祈使句中来加强语气。可译作“的确”,“确实”,“务必”,“一定”。
例如:He does run fast.
他的确跑得快。
I did go to see my grandma
yesterday.
昨天我确实去看我奶奶了。
Do come and see us when you are
free.
有空一定来玩。
Do water the flowers tomorrow.
明天务必要浇花。
Do be careful when you cross the
street.
过马路时一定要小心。
(3) every + other +(两个或两个以上)基数词+复数名词
[说明] “every + other +(两个或两个以上)基数词+复数名词”这种结构可译作
“每隔……次”。
例如:The nurse came to see the
sick man every other two hours.
护士每隔2小时来看病人一次。
The tree is planted every other ten
meters.
每隔10米种一棵树。
当我们说“每隔一天”时,我们可用下列几种表达方式:every
other day; every second day;
every two days.
[练习题]
1. Nobody but you _____ late for
school this morning.
A. is B. was C.
were D. are
2. You could have sold your car
_____ a better price.
A. in B. with C.
at D. by
3. ---Happy birthday!
---_______.
A. Have a nice time B. Say
“Hi” to you C. The same to you D.
Thank you
4. ---Bob, ______ give my regards
to your parents.
--- Yes, I _____. Thank you.
A. do, do B. does, will
C. do, will D. you, do
5. He can do nothing but
______for his father.
A. wait B. to wait
C. waiting D. waits
2. 语法句法
(1) sb. + find / think + it + adj./ n.+
(for sb.) + to do sth.
[说明]在 sb. + find / think + it
+ adj./ n. + (for sb.) + to do sth.这个句型中,
it 是形式
宾语,句末的不定式to do
sth.是真正的宾语。it后的形容词或名词是宾语补足语。
例如:I think it important for us
to study a foreign language.
我认为对我们来说学习一门外语是非常重要的。
You will find it easy to get along
with him.
你会发现和他相处很容易。
I think it our duty to obey the
laws.
我认为遵守法律是我们的义务。
(2) see / hear + 宾语 + done
[说明] 在see / hear + 宾语 +
done这个结构中,过去分词done作宾语的补足语。
它表示宾语是过去分词这一动作的承受者。
例如:I head the story told many
times.
我听到这个故事被讲了很多次了。
I saw him beaten by a big man.
我看见他被一个大个子男人打了。
能用于这种结构的动词还有:watch,
notice, feel, find, have, get等。
例如:We found two of the windows
broken .
我们发现两扇窗户被打了。
He felt a great weight taken off his
mind.
他感到去掉一件大的心事。
When she was cooking, she had her
hand burned.
她做饭时把手烫了。
[练习题]
1. ______ from Beijing to London!
A. How long way it is B.
What a long way it is
C. How long way is it D.
What a long way is it
2. It is very necessary for us
______ to English tapes.
A. listen B. listening
C. to listen D. to be listening
3. When they entered the
classroom, they found all the walls ______
white.
A. paint B. to paint
C. painting D. painted
4. ---Oh, you are still here. I
thought you had left.
--- I was _____ to leave when
you knocked at the door.
A. up B. about C.
wanting D. having
5. The children found _____
exciting to throw snowballs at each other.
A. them B. that C.
it D. the thing |
|
|
|
|
|
|