|
|
 |
*vocabulary about
earthquake 
1 earthquake wave

2 seismic belt

3 earthquake magnitude

4 the seismic focus

5 epicenter (area)

6 earthquake intensity

7 crustal movement

8 aftershock of earthquake

9 Reichter scale

*Study of earthquake 
1 seismology

2 seismologist

3 earthquake prediction

4 the seismic data

5 seismic station

6 shockproof shed

7 seismograph

8 globe

*Disasters caused by earthquakes 
1 seaquake

2 ground swell

3 volcanic eruption

4 volcanic earthquake
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
[基础知识]
1.词法
(1) sound
[说明] 1) 作名词是“声音”的意思。
例如:Did you hear a strange sound
outside last night?
你昨晚听到外边有奇怪的声音了吗?
It is known to all that light
travels faster than sound.
众所周知光速比声速快。
[说明] 2) 作行为动词,是“使……发出声响”的意思。
例如:The letter “h” in the word
“honest” is not sounded.
字母“h”在单词“honest”中不发音。
When the fire broke out late in
the night, Sam sounded the fire alarm as fast as
possible.
当深夜着火时,Sam
立即拉响了警铃。
[说明] 3) 作系动词,是“听起来,似乎”的意思,后面跟形容词、名词、like
介词短语作表语。
例如:Mike was late for school, and
the excuse he gave the teacher sounded reasonable.
Mike上课迟到了,他对老师解释的理由听起来合乎情理。
The story of Mark Twain's life
sounds interesting, would you like to read his
famous
work?
Mark Twain生平的故事听起来很有意思,你想读他的名著吗?
(2) feel
[说明]1)作及物动词,是“感到”的意思。常用
feel sb/sth do/doing 这一结构表示“感到某人/某物
在……”的意思。一些动词也能用这种结构:see,
hear, notice, watch等。
例如:I felt my heart beating faster
than before when I bumped into the thief.
当我遇到那个贼的时候,我感到我的心跳加速了。
Can you see some beautiful birds
flying in the clearly blue sky?
你能看到晴朗的蓝天中有一些美丽的鸟在飞吗?
2)
作系动词,表示给人的感觉,作“摸上去,摸起来”解。
例如:The silk feels soft. I'd like to
measure my daughter a new dress.
这块丝绸摸上去很柔软,我想给女儿裁条连衣裙。
feel happy/ strange/ ill/ cold/
worried/ sorry
(3) a number of / the number of
[说明]这两个短语意思不同,注意不要混淆。
1) a number of, 还可以用 a
large / small number of ,是“许多,若干”的意思。
of
+名词复数,修饰主语时,谓语动词用复数形式。
例如:A number of students are
standing outside the office waiting for their turn
to recite
the text.
许多学生站在老师办公室外按顺序等候背书。
There are a large number of new
books in our school library this term.
这学期我们学校图书馆有许多新书。
2) the number of, 作“……的数量”解,后接名词复数,the
number of 在句中作主语时,
谓语动词用单数。
例如:The number of the college
students is increasing year by year.
大学生的数量逐年增加。
The number of comrades absent
from the meeting was surprising.
没有到会的同志人数很惊人。
(4) as many as; as much as
[说明]英语中在表示数量的词语前,习惯上加as
many as, as much as等来加强语气。as much as
常用在“雨量、水量、时间量、重量、钱数、价格”等方面,表示总量和单位量的大小;as
many
as
常用在人或物的具体数量前,侧重于具体数目,意思是“和……一样多”,“多达……”。
例如:Along Amazon rain is plentiful,
often as much as seventy inches every year.
亚马逊河流域雨水充足,年降水量常达70英寸之多。
The hightest price of a jacket
in the shop is as much as 5,000 yuan.
该店夹克的最高价达5000元。
In the countries of Africa,
there are as many as 700 languages.
非洲国家的语言多达700种。
The kings of Egypt built as many
as 80 pyramids.
埃及国王们建造的金字塔多达80座。
(5) not…but…
[说明]连接两个并列成分,表示转折关系,否定前面的内容。意思为“不是……,而是……”。
后面一般省略前面出现过的词语。
例如:Sam did not do any homework last
Sunday, but played PC games all day.
Sam上个星期天没有做任何功课,而是玩了一天PC游戏。
The milu deer is not blind in
the left eye but in the right eye.
那只麋鹿不是左眼瞎而是右眼瞎。
(6) cut off
[说明]是“切断”、“停止”、“砍掉”的意思。cut
off 除表示“从某一物的一端切去或剪去一部分”外,
还常表示抽象意义的“切断”电路、电源、线路,“断绝”某种东西的供应等。
例如:Be careful! Don't cut your
finger off.
当心,别切了手指。
The line was cut off while I was
talking to a friend by telephone.
在我和朋友通电话时线路被切断了。
(7) at the speed of
[说明] at 是介词,表示“速度、速率”,“以/按……速度”,常用于“at
the speed /rate of ”
这一结构。
例如:The train runs at ( the rate of
) 160 km an hour since 2000.
自从2000年以来火车的时速达到了每小时160公里。
The scooter goes much slower
than the car at (the speed of ) 30 km an hour.
轻骑的速度比小汽车慢的多,大约每小时30公里。
[练习题]
1. The number of people killed in the
accident _____ 56, so we can say that a number of
people _____ killed in the accident.
A. were; were B. were; was C.
was; were D. was; was
2. To their luck, the earthquake didn't
happen in the center of the city. It happened ____
about 60 kilometres away.
A. at B. 不填 C.
in D. to
3. The doorkeeper noticed the man _____
the office alone very late last night.
A. leaving B. to leave C.
left D. leave
4. The road to the mountains _____ by the
heavy snow for almost a week.
A. have been cut off B. has
been cut off
C. has been cut down D. have
been cut down
5. How _____ the music sounds and how
_____ Mary's voice is!
A. sweet, good B. sweet, well
C. sweetly, good D. sweetly, well
2.语法句法
学习由 who/ whom/ while/ that
引导的定语从句。
引导定语从句的关系代词有 that,
which, who, whom, whose和as。若先行词为人,在从句中作主语,
关系词选用who或that;作宾语,可选用who,
whom或that,且常可省略。若先行词为物,在从句中作
主语或宾语时,关系词则用which或that,且作宾语时可省略。
1)The girl who/that told me the news is not
here now.
告诉我消息的那个女孩现在不在这儿。
2)A clock is a machine that/which tells us
the time.
钟是一种告诉我们时间的机械。
3)The man who/whom/that you talked about
just now is my friend.
你刚才说起的那个人是我的朋友。 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
[拓展知识]
1.词法
(1) 倍数的表达法
[说明]A is … times + adj. /adv. (比较级)
+ than + B.
此句型表示“A比B大(小、高、低等)……倍”。
例如:The number of students in our
school is three times larger than that in theirs.
我们学校的学生数量比他们学校的多三倍。
The sun is a large blazing ball, a
million times larger than the earth.
太阳是一个庞大炽燃球体,它比地球大一百万倍。
另外还可以用“A is … times as
+ adj./ adv. (原级) + as B”句型表示“A是B的……的倍”。
例如:This concert hall is four
times as large as that one.
这个音乐堂是那个音乐堂的四倍大。
This lake is twice as wide as that
one.
这个湖的宽是那个湖的两倍。
(2) afraid
[说明]afraid 是形容词。
be afraid to do sth. 表示“不敢去做某事”,即“怕而不敢”。
be afraid of sth. /doing sth.表示“害怕、忧虑、担忧”,后可接名词、动名词,它着重强调对可
能产生的后果担忧或忧虑。
be afraid that-clause表示“恐怕”,即表示歉意、回绝或引出不好的消息,是一种委婉语气。
例如:Are you afraid to go home at
night alone?
你单独回去害怕吗?
I'm afraid to see her. She is very
strict with me.
我不敢见她。她对我的要求特别严。
People now are not very much afraid of
earthquakes.
现在人们并不是很害怕地震。
She was afraid of waking her husband
up.
她担心会吵醒她的丈夫。
I'm afraid (that) I must go now.
恐怕现在我得走了。
I'm afraid I can't help you.
恐怕我不能帮你的忙。
(3) when, while, as 的区别
[说明]作连词时,when,while和as都有“当……时候”的意义,引导时间状语从句,但应注意它们
的区别。
1)
如主句谓语动词表示的是短暂动作,从句时间状语指一段时间,三者可通用。
例如:Peter came in while /as I was
watching TV.
当Peter进来的时候我正在看电视。
I was watching TV when Peter came in.
当Peter进来时我正在看电视。
2) as 和 when
可与非延续性动词连用,而 while
只能与延续性动词连用。
例如:He came in when/ as I was
going to bed.
我正要上床睡觉,他进来了。
3) as 和 while可用来指一段时间,但
as
强调主句与从句表示的动作同时发生,while强调主
句表示的动作是在 while
从句的动作延续中发生。
例如:As my mother sang those old
songs, tears ran down her cheeks.
当我妈妈唱起那些老歌时,眼泪顺着她的脸颊流了下来。
I came in while he was reading an
interesting book in his room.
我进来的时候他正在房间里看一本有趣的书。
[练习题]
1. As a result of the worker's
hardworking, they produced _____ new products last
year as they did the year before.
A. twice as many B. as twice
many C. as many twice D. twice so many
2. _____ her scooter has been lost. We
can't find it anywhere.
A. I am afraid B. I hope
C. I wonder D. I don't think
3. Growing corn doesn't need _____
growing rice.
A. as much water as B. as
much water like
C. much water as D. too
much water as
4. I was just about to speak _____ Jack
stood up and began his long dull talk.
A. while B. but C.
however D. when
5. Mary didn't speak English with other
classmates for she was afraid _____ mistakes
and _____.
A. to make, to laugh at
B. making, laughing at
C. to be make, to be laughed at
D. of making, being laughed at
2.语法句法
定语从句关系词的选择并不难,关键是弄清先行词是人还是物,在从句中作什么成分以及句式结构
等。但若先行词在从句中作相同的成分,引导词又该如何判断呢?
(1) 先行词为物时,which与that的区别
在下列情况下,通常只用 that
。
1) 当先行词为 all, much, little,
few, nothing 等不定代词时。
例如:She did all that she could to
help him.
她尽她的所能帮助他。
Is there anything else that
you don't understand?
你还有什么不明白的吗?
2) 当先行词由no, any, all, much,
little, the only, the very等修饰时。
例如:This is the very book that I
want.
这正是我想要的书。
In my opinion the only thing
that we could do was to wait.
依我看我们唯一能做的就是等。
3)
当先行词由序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。
例如:This is the best hotel in the
city that I know.
这是我所知道这个城市中最好的宾馆。
4)
当先行词既有人又有物时。
例如:He talked on and on happily
of the men and books that interested him.
他高兴地聊着他感兴趣的人和书。
(2) 先行词为人时,who与that的区别。
1)
若先行词在从句中作表语或主句是以who引起的特殊疑问句时,关系代词用that。
例如:He isn't the man that he used
to be.
他已经不是原来的他了。
Who is the man that is standing
there talking to our headmaster?
站在那边和校长说话的人是谁?
2) 若先行词为he, those, anyone等表示一类人或在分隔式定语从句中,关系词一般用who。
例如:He who laughs last laughs
best.
谁笑到最后,谁笑的最好。
I met a foreigner in the
shopping center yesterday who could speak in
Chinese
very well.
昨天我在购物中心遇到一个中文说的特别好的外国人。
[练习题]
1. She is the woman _____ lives next
door.
2. I have just met an old man _____ I
saw last week.
3. The tall man _____ is standing there
is a good doctor.
4. The passengers and the suitcases
_____ were still waiting had to take another ship.
5. It was the only shop _____ hadn't
closed down at that time.
6. Is this the shop _____ sells
children's clothes?
7. All _____ can be done has been done.
8. Which is the car _____ hit the boy
badly?
9. This is the smallest computer _____
can be found in the world now.
10.There is nothing _____ is too
difficult for me. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |

An earthquake
happened
in Taiwan in 1999. |
Earthquake
Earthquake is a shaking of the ground
caused by the sudden breaking and shifting
of large sections of the earth's rocky
outer shell. Earthquakes are among the
most powerful events on earth, and their
results can be terrifying. A severe
earthquake may release energy 10,000 times
as great as that of the first atomic bomb.
Rock movements during an earthquake can
make rivers change their course.
Earthquakes can trigger landslides that |
cause
great damage and loss of life. Large
earthquakes beneath the ocean can create a
series of huge, destructive waves called
tsunamis that flood coasts for many miles.
Earthquakes almost never kill people
directly. Instead, many deaths and
injuries in earthquakes result from
falling objects and the collapse of
buildings, bridges, and other structures.
Fire resulting from broken gas or power
lines is another major danger during a
quake. Spills of hazardous chemicals are
also a concern during an earthquake.
|

A great fire may be caused
by the earthquake.
|

People were injured
in the quake. |
The
force of an earthquake depends on how much
rock breaks and how far it shifts.
Powerful earthquakes can shake firm ground
violently for great distances. During
minor earthquakes, the vibration may be no
greater than the vibration caused by a
passing truck.
On average, a powerful earthquake
occurs less than once every two years. At
least 40 moderate earthquakes cause damage
somewhere in the world each year. About
40,000 to 50,000 small earthquakes-large
enough to be felt but not damaging-occur
annually. |
Earthquakes can damage buildings,
bridges, dams, and other structures, as
well as many natural features. Near a
fault, both the shifting of large blocks
of the earth's crust, called fault
slippage, and the shaking of the ground
due to seismic waves cause destruction.
Away from the fault, shaking produces most
of the damage. Undersea earthquakes may
cause huge tsunamis that swamp coastal
areas. Other hazards during earthquakes
include rockfalls, |

Roads were destroyed
in the quake.
|
 |
ground
settling, and falling trees or tree
branches.
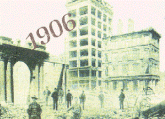
On
Apr. 18, 1906, San Francisco suffered a
major earthquake; the resulting 3-day fire
razed the core of the city. The 1906 San
Francisco earthquake kills 700.
|
| The
San Francisco earthquake of 1989 |
| The
San Francisco earthquake of 1989 occurred
along the San Andreas Fault, a major
fracture in the Earth's crust that runs
about 80 km (50 mi) east of the California
coast from southern California north to
San Francisco, where it goes out to sea. |
 |
 |
Oakland
Bay Bridge collapsed during the earthquake
that rocked the region in 1989. The
collapse of a nearby double-decker highway
caused many deaths. |
|
|
|
India, Pakistan quake kills over 100 |
A strong
earthquake rocked Pakistan and India, knocking
over buildings and houses. Officials confirmed at
least 140 deaths.
  
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|